Difference between revisions of "LiteCommerce:Modules and Decorators"
(Created page with 'A module adds some extra functionality or changes the default LiteCommerce behavior by “runtime decorating” of the original code, so there is no need for changing or patching…') |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Each module must include the <u>classes/modules/ModuleName</u> directory, which should contain the following files: | Each module must include the <u>classes/modules/ModuleName</u> directory, which should contain the following files: | ||
| − | {| class="wikitable" | + | {| class="wikitable" width=800 |
| − | | ModuleName.php | + | | '''ModuleName.php''' |
| the main module class responsible for module installation and initialization. | | the main module class responsible for module installation and initialization. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | MANIFEST | + | | '''MANIFEST''' |
| the module descsription file. A typical MANIFEST file looks like | | the module descsription file. A typical MANIFEST file looks like | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{Note|please, contact us to obtain unique module identifier for your custom module. This reduces the risk of collisions between third-party and original modules.}} | {{Note|please, contact us to obtain unique module identifier for your custom module. This reduces the risk of collisions between third-party and original modules.}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | install.php | + | | '''install.php''' |
| an optional PHP file, executing during installation. | | an optional PHP file, executing during installation. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | install.sql | + | | '''install.sql''' |
| an optional SQL patch file, executing during installation. | | an optional SQL patch file, executing during installation. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | post-install.php | + | | '''post-install.php''' |
| an optional file, which is called just after the installation is complete and typically contains further user instructions. | | an optional file, which is called just after the installation is complete and typically contains further user instructions. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | classes.lst | + | | '''classes.lst''' |
| required index of all module classes. Is generated automatically with classes list builder. | | required index of all module classes. Is generated automatically with classes list builder. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
Once you have added a decorator to a class, it will replace the original class in future, e.g. the func_new function call will produce the decorated class instance instead of an original class instance. Decorators are typically registered in the module initialization method with the addDecorator module method, as it is shown in the listing below. Decorator classes must be declared to extend original classes. | Once you have added a decorator to a class, it will replace the original class in future, e.g. the func_new function call will produce the decorated class instance instead of an original class instance. Decorators are typically registered in the module initialization method with the addDecorator module method, as it is shown in the listing below. Decorator classes must be declared to extend original classes. | ||
| − | Example 2.2 Decorating the Product class from a module | + | '''Example 2.2 Decorating the Product class from a module''' |
<source> | <source> | ||
| Line 131: | Line 131: | ||
class MyModule extends Module // the module main class | class MyModule extends Module // the module main class | ||
{ | { | ||
| − | // module initialization method | + | // module initialization method |
| − | // called at startup | + | // called at startup |
| − | function init() | + | function init() |
| − | { | + | { |
| − | parent::init(); | + | parent::init(); |
| − | // the same as | + | // the same as |
| − | // func_add_decorator("Product", "Module_MyModule_Product"); | + | // func_add_decorator("Product", "Module_MyModule_Product"); |
| − | // but in a more preferred manner | + | // but in a more preferred manner |
| − | $this->addDecorator("Product", "Module_MyModule_Product"); | + | $this->addDecorator("Product", "Module_MyModule_Product"); |
| − | } | + | } |
} | } | ||
| Line 152: | Line 152: | ||
Of course it is possible to extend a class without replacing it, if you just inherit it and do not register a decorator. | Of course it is possible to extend a class without replacing it, if you just inherit it and do not register a decorator. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:LiteCommerce developer guide]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:24, 5 February 2010
A module adds some extra functionality or changes the default LiteCommerce behavior by “runtime decorating” of the original code, so there is no need for changing or patching core php files. Modules come in .tar files and can be easily installed, removed, and deactivated. Modules serve a basic LiteCommerce customization tool, because they do not require any changes to the LiteCommerce core files and simplify upgrading customized websites.
Each module must include the classes/modules/ModuleName directory, which should contain the following files:
| ModuleName.php | the main module class responsible for module installation and initialization. |
| MANIFEST | the module descsription file. A typical MANIFEST file looks like
module_id=3000 name=Promotion description=”Promotional package: special offers, etc.” enabled=1 version=2.0 dependencies= The MANIFEST file specifies a unique module id, module name (no spaces or special characters allowed), description, whether the module is activated by default (1) or not (0), its version and a comma-separated list of modules this module depends on. Note: please, contact us to obtain unique module identifier for your custom module. This reduces the risk of collisions between third-party and original modules.
|
| install.php | an optional PHP file, executing during installation. |
| install.sql | an optional SQL patch file, executing during installation. |
| post-install.php | an optional file, which is called just after the installation is complete and typically contains further user instructions. |
| classes.lst | required index of all module classes. Is generated automatically with classes list builder. |
The main class must be inherited from the Module and can redeclare the base Module class methods and properties. You can use the Module class description and free modules available from the LiteCommerce web site as a good example for main module class.
Modules use class inheritance to change LiteCommerce functionality. Thus a module does not change the LiteCommerce php code itself, however it inherits and overrides the kernel LiteCommerce class methods. Several modules can modify the same kernel class, so that module classes are inherited from each other, creating an inheritance chain.
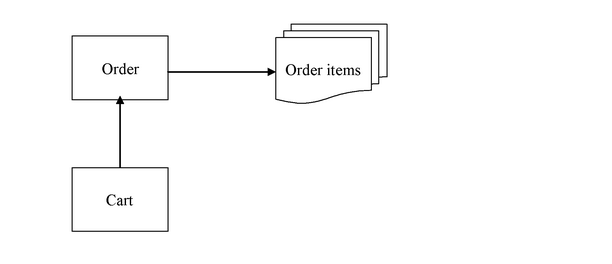
Let us consider an example that illustrates this technique. The example below illustrates three of the kernel LiteCommerce classes, namely Order, Cart and OrderItem. The Cart class extends the Order, which is denoted by an arrow. An order can have a number of items, and this association is also shown by an arrow.
Figure 2.1 LiteCommerce kernel classes
We also have three modules installed -- ProductOptions, Promotion, and GiftCertificates, which modify the considered classes. The table below shows which modules extend which classes.
Table 2.1 Modules that extend LiteCommerce classes.
| Order | Cart | OrderItem | |
| ProductOptions | x | ||
| Promotion | x | x | x |
| GiftCertificates | x | x |
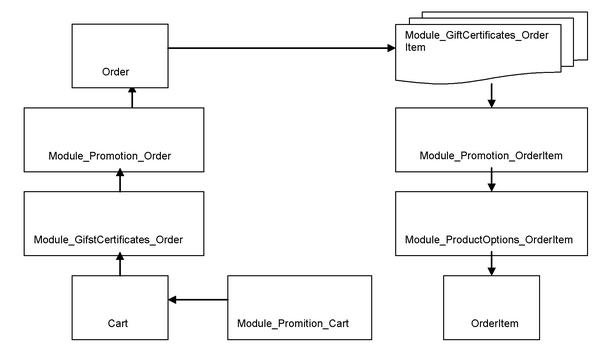
When LiteCommerce starts, it reads the information about all active modules and changes the class inheritance scheme so that module classes, extending the same object, are organized in a chain. The figure below represents the inheritance scheme in the given example.
Figure 2.2 Class structure when the modules are active
In order to build chains dynamically, LiteCommerce reads class source files, changes the extends clause, renames the classes by appending the “__” postfix and writes the resulting PHP code in the “var/run/classes” directory for future use. For example, the following definition, appearing in the GiftCertificate module:
Example 2.1 Module inheritance order.
class Module_GiftCertificate_Order extends Order
{
...is changed to:
class Module_GiftCertificate_Order__ extends Module_Promotion_Order__
{
...Compiled classes are put into var/run/classes/modules/GiftCertificates/kernel. Each time you turn modules on or off, LiteCommerce rebuilds the var/run/classes files. From now on, each time you call func_new("Order"), an instance of the Module_GiftCertificate_Order__ class is created. Users can use func_new transparently to create instances. To make it even more transparent, LiteCommerce defines some functions that operate on classes, shown in the table below:
Table 2.2 LiteCommerce class manipulation functions
| function name | description |
|---|---|
| func_class_exists($name) | checks for the class existence (no need to require() it |
| func_new($name[,...]) | creates a new class instance |
| func_is_a($child, $parent) | checks that the $child class extends the $parent class |
| func_add_decorator ($decorated, $decorator) | adds the class $decorator to the inheritance chain of the class $decorated. |
The module classes that replace the core classes are also called decorators
Once you have added a decorator to a class, it will replace the original class in future, e.g. the func_new function call will produce the decorated class instance instead of an original class instance. Decorators are typically registered in the module initialization method with the addDecorator module method, as it is shown in the listing below. Decorator classes must be declared to extend original classes.
Example 2.2 Decorating the Product class from a module
// in classes/modules/MyModule/MyModule.php
class MyModule extends Module // the module main class
{
// module initialization method
// called at startup
function init()
{
parent::init();
// the same as
// func_add_decorator("Product", "Module_MyModule_Product");
// but in a more preferred manner
$this->addDecorator("Product", "Module_MyModule_Product");
}
}
// in classes/modules/MyModule/kernel/Product.php
class Module_MyModule_Product extends Product
{
...
}Of course it is possible to extend a class without replacing it, if you just inherit it and do not register a decorator.